The Waste Framework Directive: Directive 2008/98/EC
Directive 2008/98/EC sets the basic concepts and definitions related to waste managament, such as definitions of waste, recycling, recovery. It explains when waste ceases to be waste and becomes a secondary raw material (so called end-of-waste criteria), and how to distinguish between waste and by-products.
The Directive lays down some basic waste management principles: it requires that waste be managed without endangering human health and harming the environment, and in particular without risk to water, air, soil, plants or animals, without causing a nuisance through noise or odours, and without adversely affecting the countryside or places of special interest.
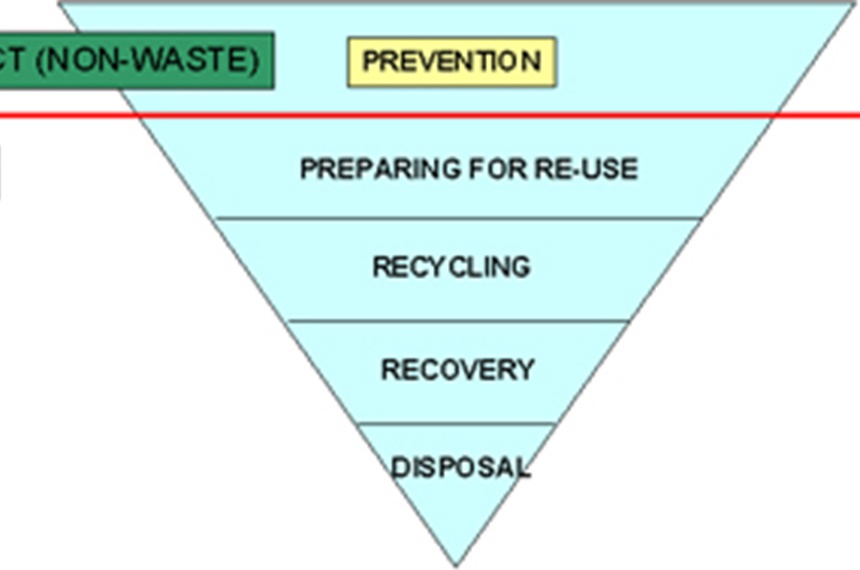
According to the Directive, waste legislation and policy of the EU Member States shall apply as a priority order the following waste management hierarchy:
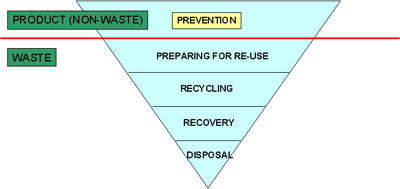
The Directive introduces the "polluter pays principle" and the "extended producer responsibility". It incorporates provisions on hazardous waste and waste oils (old Directives on hazaroud waste and waste oils being repealed with the effect from 12 December 2010), and includes two new recycling and recovery targets to be achieved by 2020: 50% preparing for re-use and recycling of certain waste materials from households and other origins similar to households, and 70% preparing for re-use, recycling and other recovery of construction and demolition waste.
The Directive requires that Member States adopt waste management plans and waste prevention programmes.
Source: European Commission
Find out more about this topic here.

Follow us on